Fwd Emails sent to Domain to Gmail
You can receive emails sent to your domain by using two processes within AWS.
- Have SES store the email in an S3 bucket
- Trigger Lambda function to create an email to forward to gmail with the email content that was received. The Lambda function literally copies all the content/attachments, and creates your own email to send to a SES verified domain.
Make sure you have already verified the domain and the personal email address you want to forward emails to.
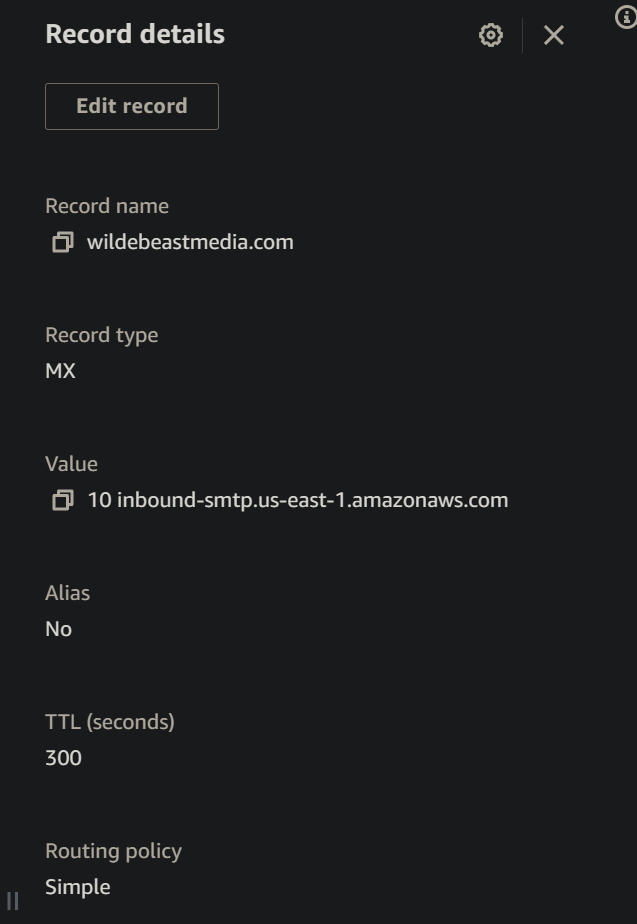
Create MX Record in Route 53¶
Add the following MX record to the DNS configuration for your domain:
10 inbound-smtp.<regionInboundUrl>.amazonaws.com
Replace <regionInboundUrl> with the URL of the email receiving endpoint for the AWS Region that you use Amazon SES in. For a complete list of URLs, see AWS Service Endpoints – Amazon SES in the AWS General Reference.
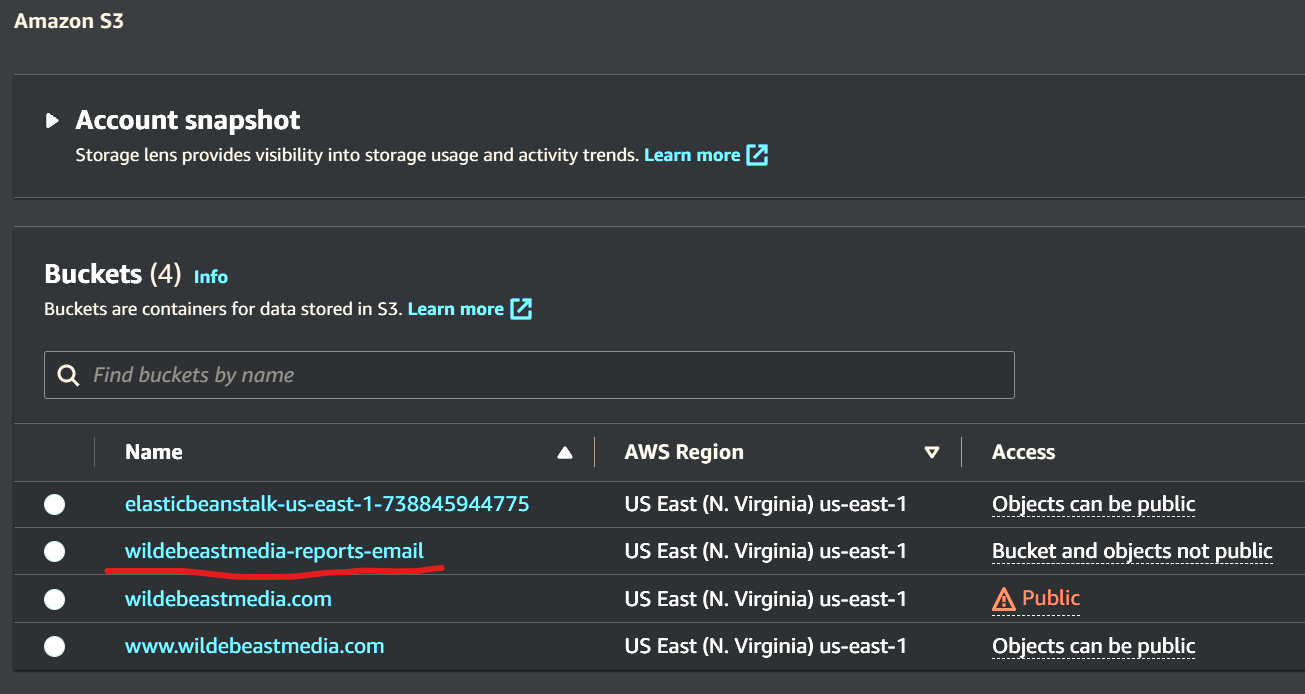
Create an S3 Bucket to Store Emails¶
Apply the following policy to the bucket in the Permissions tab:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllowSESPuts",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "ses.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "s3:PutObject",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::<bucketName>/*",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"aws:Referer": "<awsAccountId>"
}
}
}
]
}
In the policy, make the following changes:
- Replace <bucketName> with the name of your S3 bucket.
- Replace <awsAccountId> with your AWS account ID.
The name of your S3 Bucket is how it appears in your list of Buckets. Note that mine is called wildebeastmedia-reports-emails
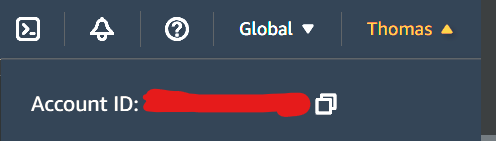
Your account ID can be found in the top right of the window. Remove the dashes from the ID in the policy.
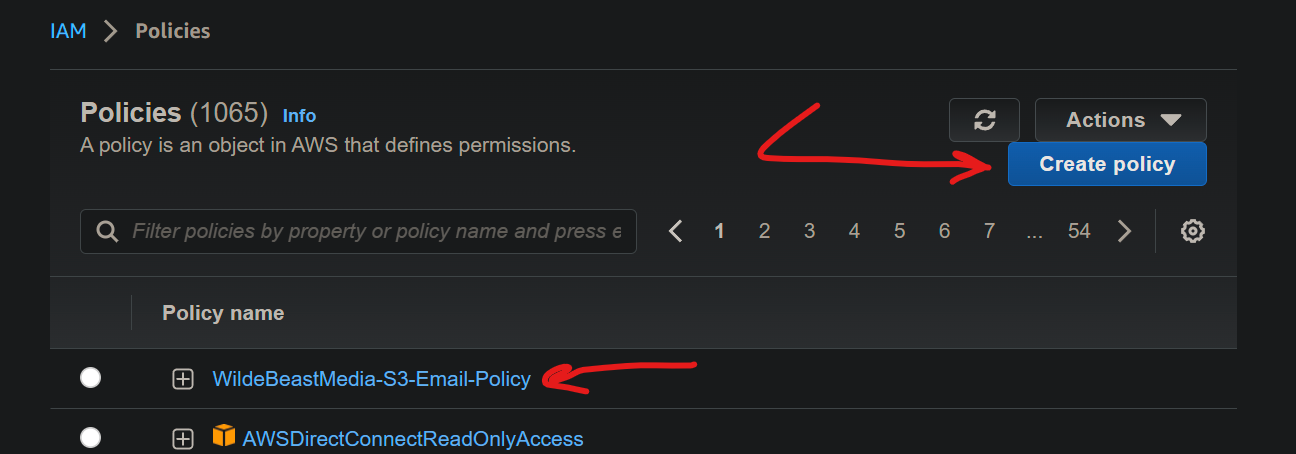
Create an IAM Policy and Role¶
Create IAM Policy¶
We want to create a specific role for the Lambda function with limited permissions, specific the ability to send emails through SES and store emails in the S3 Bucket we created.
Go to IAM/Policies and hit Create policy. I named mine <domain>-S3-Email-Policy
Add the following JSON permission to the policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor1",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject",
"ses:SendRawEmail"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::<bucketName>/*",
"arn:aws:ses:<region>:<awsAccountId>:identity/*"
]
}
]
}
- Replace
with the name of the S3 bucket that you created earlier. - Replace
with the name of the AWS Region that you created the bucket in. - Replace
with your AWS account ID.
Create IAM Role¶
Create a new IAM role. Attach the policy that you just created to the new role. I'm calling the role <domain>-Lambda-Email-Role
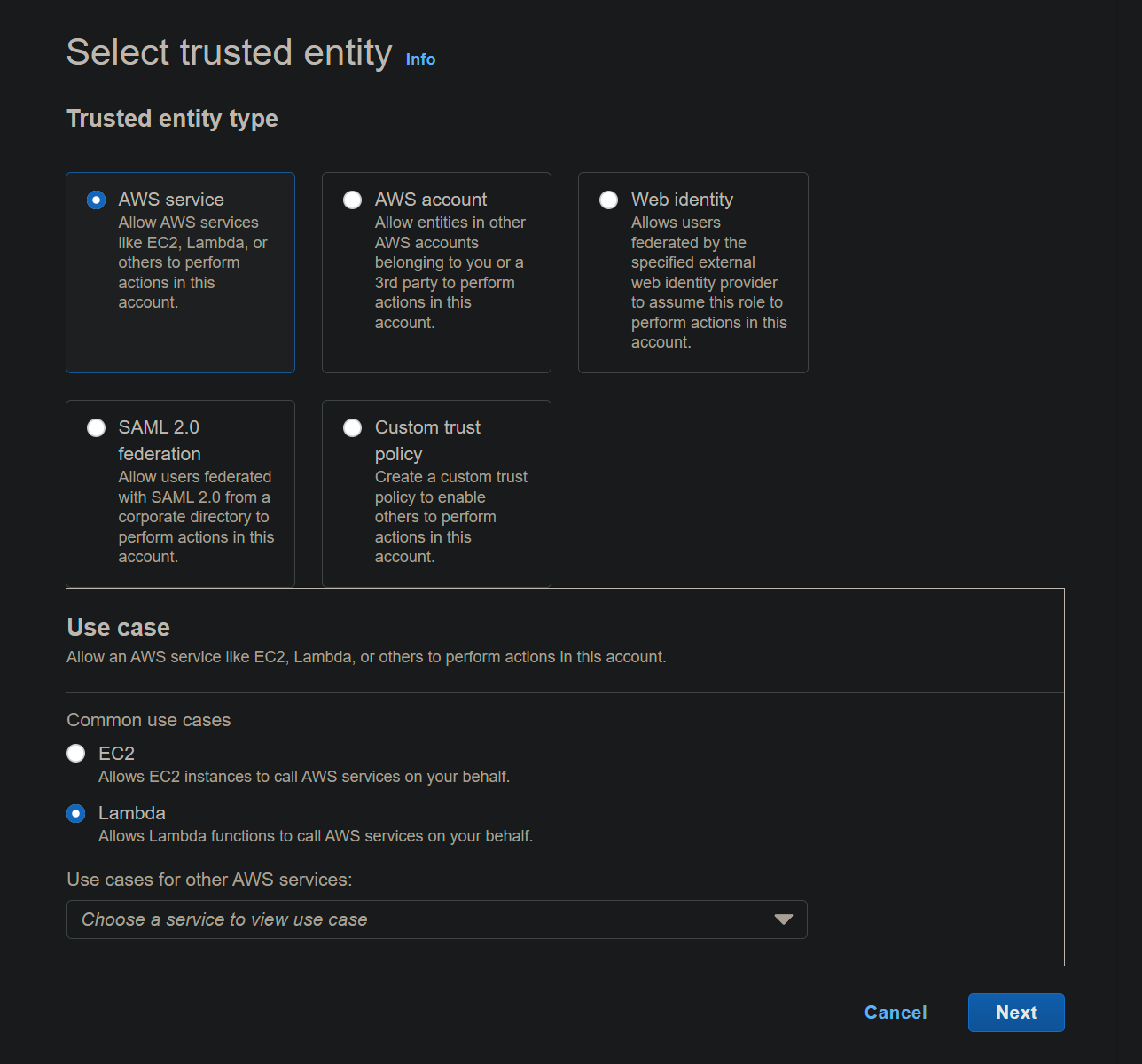
The trusted entity type will be AWS service and the use case is Lambda
Choose the policy we created to attach to our new role.
Create the Lambda Function¶
Function Overview¶
The Lambda Function is a Python script that will reach into our S3 bucket, scrape the email content, add it to an email draft, and send it to our personal email.
In the Lambda console, create a new Python 3.7 function from scratch. For the execution role, choose the IAM role that you created earlier. I am naming the function <domain>-S3-Email
Here is the overview
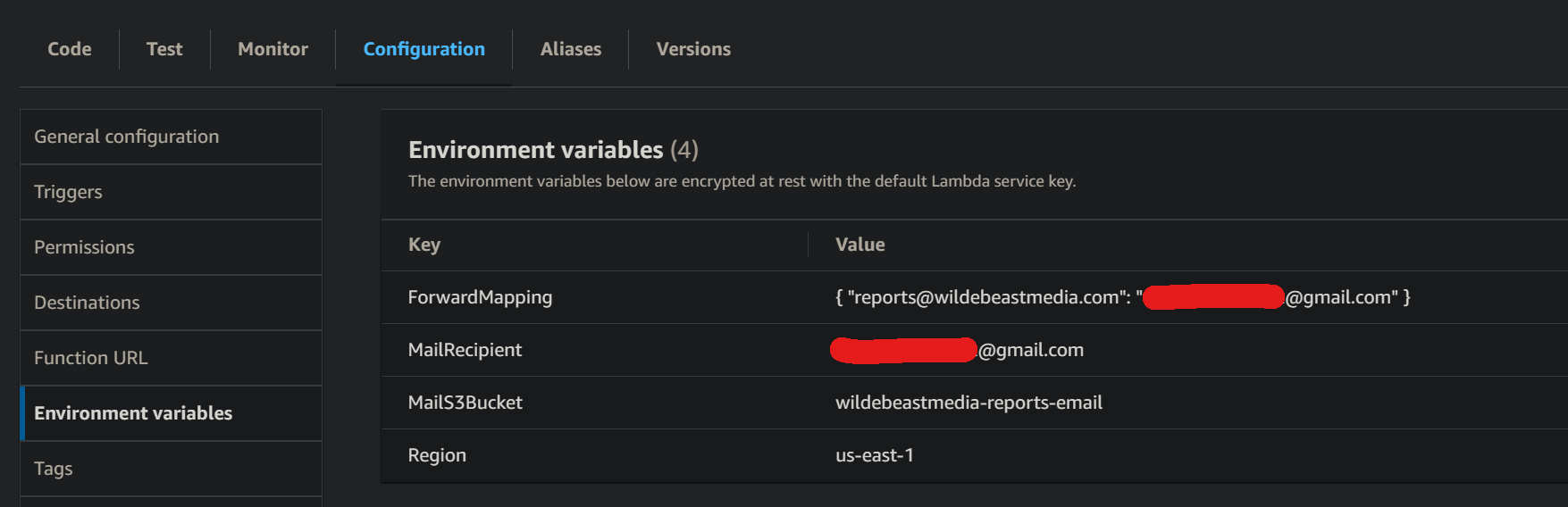
Add configuration Environmental Variables¶
Scroll down to the code area and click on Configuration. We are going to set up some environmental variables that the python script we use. Let's define the following
ForwardMappingMailRecipientMailS3BucketRegion
ForwardMapping is a json object where we can specify where certain email address of the domain should get forwarded to. For example, we might want emails sent to [email protected] to be forwarded to [email protected], while emails sent to [email protected] should be forwarded to [email protected].
MailRecipient is the default forwarding address for any and all domain addresses not explicitly stated in ForwardMapping.
Here is my configuration:
Add the Python Code¶
import os
import boto3
import email
import re
import json
from botocore.exceptions import ClientError
from email.mime.multipart import MIMEMultipart
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
from email.mime.application import MIMEApplication
region = os.environ['Region']
def get_message_from_s3(message_id):
incoming_email_bucket = os.environ['MailS3Bucket']
# incoming_email_prefix = os.environ['MailS3Prefix']
# if incoming_email_prefix:
# object_path = (incoming_email_prefix + "/" + message_id)
# else:
# object_path = message_id
object_path = message_id
object_http_path = (f"http://s3.console.aws.amazon.com/s3/object/{incoming_email_bucket}/{object_path}?region={region}")
# Create a new S3 client.
client_s3 = boto3.client("s3")
# Get the email object from the S3 bucket.
object_s3 = client_s3.get_object(Bucket=incoming_email_bucket,
Key=object_path)
# Read the content of the message.
file = object_s3['Body'].read()
file_dict = {
"file": file,
"path": object_http_path
}
return file_dict
def create_message(file_dict, original_recipient, forward_address):
sender = original_recipient
# Parse the email body.
mailobject = email.message_from_string(file_dict['file'].decode('utf-8'))
# Extract the original email's details
original_from = mailobject['From']
original_subject = mailobject['Subject']
original_body = extract_body(mailobject)
# Create a new subject line.
subject = "Fwd: " + original_subject
# Construct the forwarded email body
body_text = f"""\
Forwarded message:
From: {original_from}
To: {original_recipient}
Subject: {original_subject}
{original_body}
"""
# Create a MIME container.
msg = MIMEMultipart()
# Create a MIME text part.
text_part = MIMEText(body_text, _subtype="plain")
# Attach the text part to the MIME message.
msg.attach(text_part)
# Attach original email's attachments
if mailobject.is_multipart():
for part in mailobject.walk():
if part.get_content_maintype() == 'multipart':
continue
if part.get('Content-Disposition') is None:
continue
msg.attach(part)
# Add subject, from, and to lines.
msg['Subject'] = subject
msg['From'] = sender
msg['To'] = forward_address
message = {
"Source": sender,
"Destinations": forward_address,
"Data": msg.as_string()
}
return message
def extract_body(mailobject):
if mailobject.is_multipart():
for part in mailobject.walk():
if part.get_content_type() == "text/plain":
return part.get_payload()
else:
return mailobject.get_payload()
def send_email(message):
aws_region = os.environ['Region']
# Create a new SES client.
client_ses = boto3.client('ses', region)
# Send the email.
try:
#Provide the contents of the email.
response = client_ses.send_raw_email(
Source=message['Source'],
Destinations=[
message['Destinations']
],
RawMessage={
'Data':message['Data']
}
)
# Display an error if something goes wrong.
except ClientError as e:
output = e.response['Error']['Message']
else:
output = "Email sent! Message ID: " + response['MessageId']
return output
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Get the unique ID of the message. This corresponds to the name of the file
# in S3.
message_id = event['Records'][0]['ses']['mail']['messageId']
print(f"Received message ID {message_id}")
# Get the recipient address from the event object
recipient = event['Records'][0]['ses']['receipt']['recipients'][0]
# Load the forwarding mapping from the environment variable
forward_mapping = json.loads(os.environ['ForwardMapping'])
# Get the forwarding address for the recipient
forward_address = forward_mapping.get(recipient)
# Use the default forwarding address if no specific address is found
if not forward_address:
default_forward_address = os.environ['MailRecipient']
forward_address = default_forward_address
# Retrieve the file from the S3 bucket.
file_dict = get_message_from_s3(message_id)
# Create the message.
message = create_message(file_dict, recipient, forward_address)
# Send the email and print the result.
result = send_email(message)
print(result)
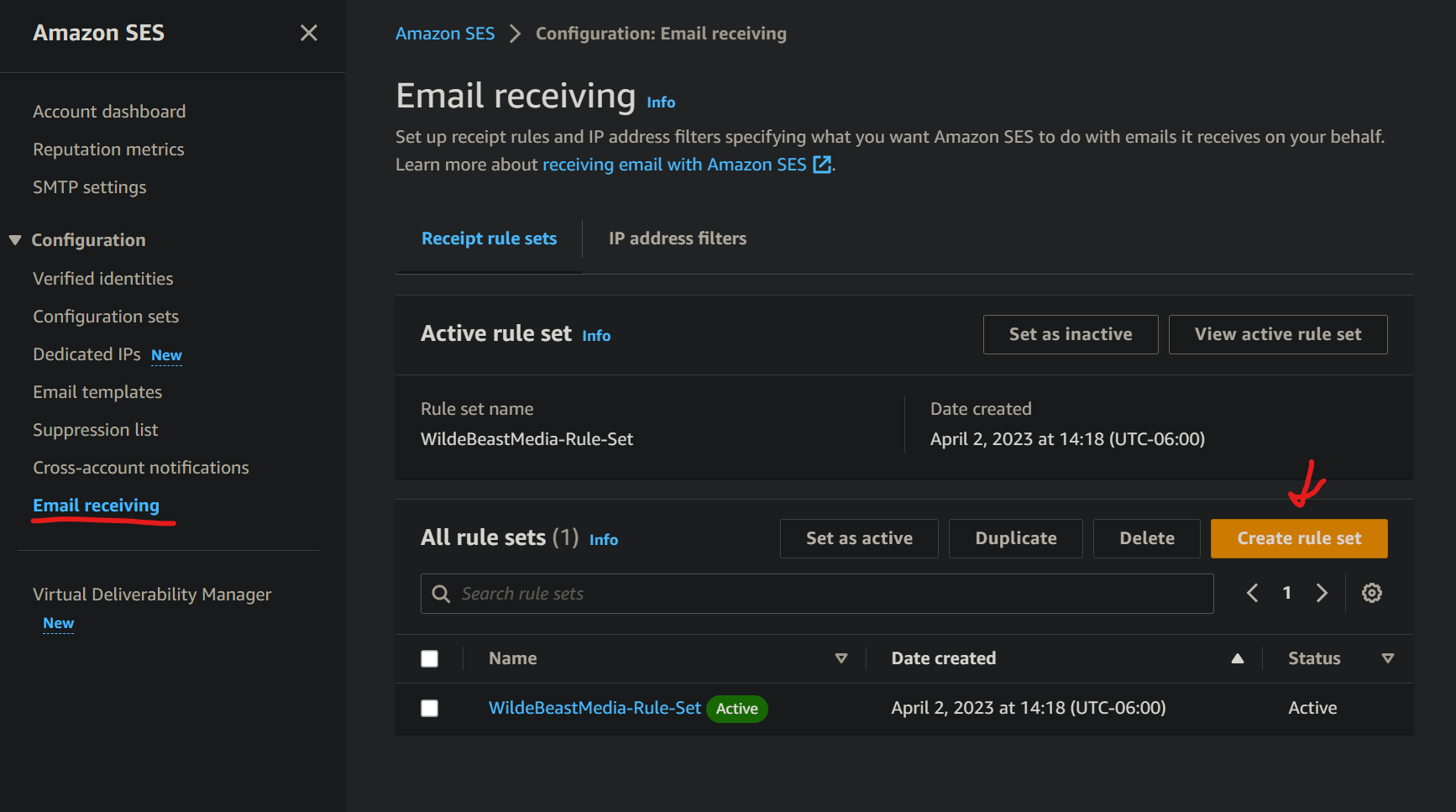
Create SES Receipt Rule Set¶
In Simple Email Services (SES), we will create a Rule-Set that basically says whenever an email is received to our domain, store the Email in an S3 bucket, then invoke our Lambda Function on the Email. The Lambda function of course performs our logic of creating a forwarded email and sending it to our personal email.
In the Amazon SES console, create a new Receipt Rule Set. I'm calling mine <domain>-Rule-Set.
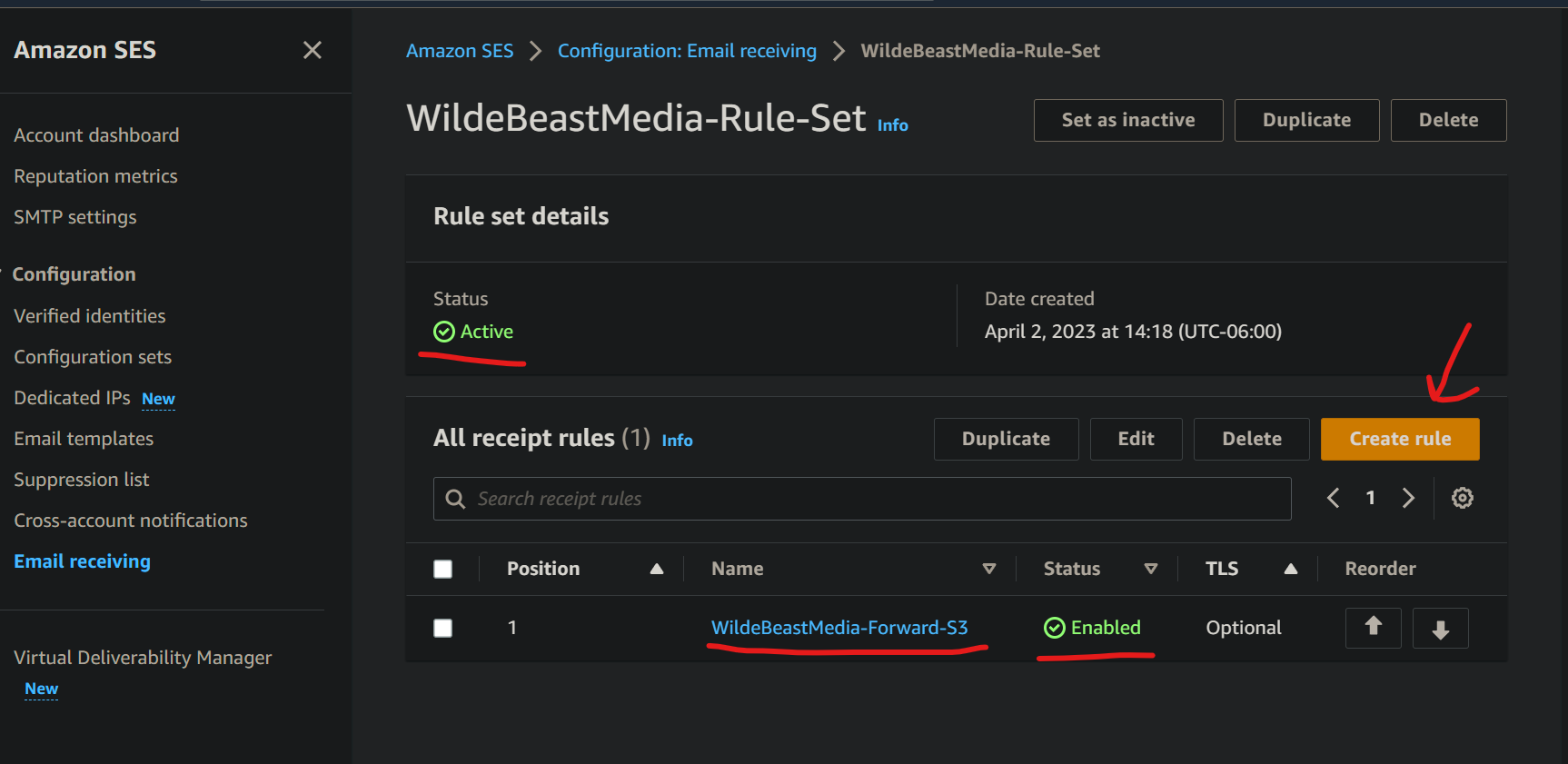
In the Receipt Rule Set that you just created, add a Receipt Rule. I'm calling mine <domain>-Forward-S3.
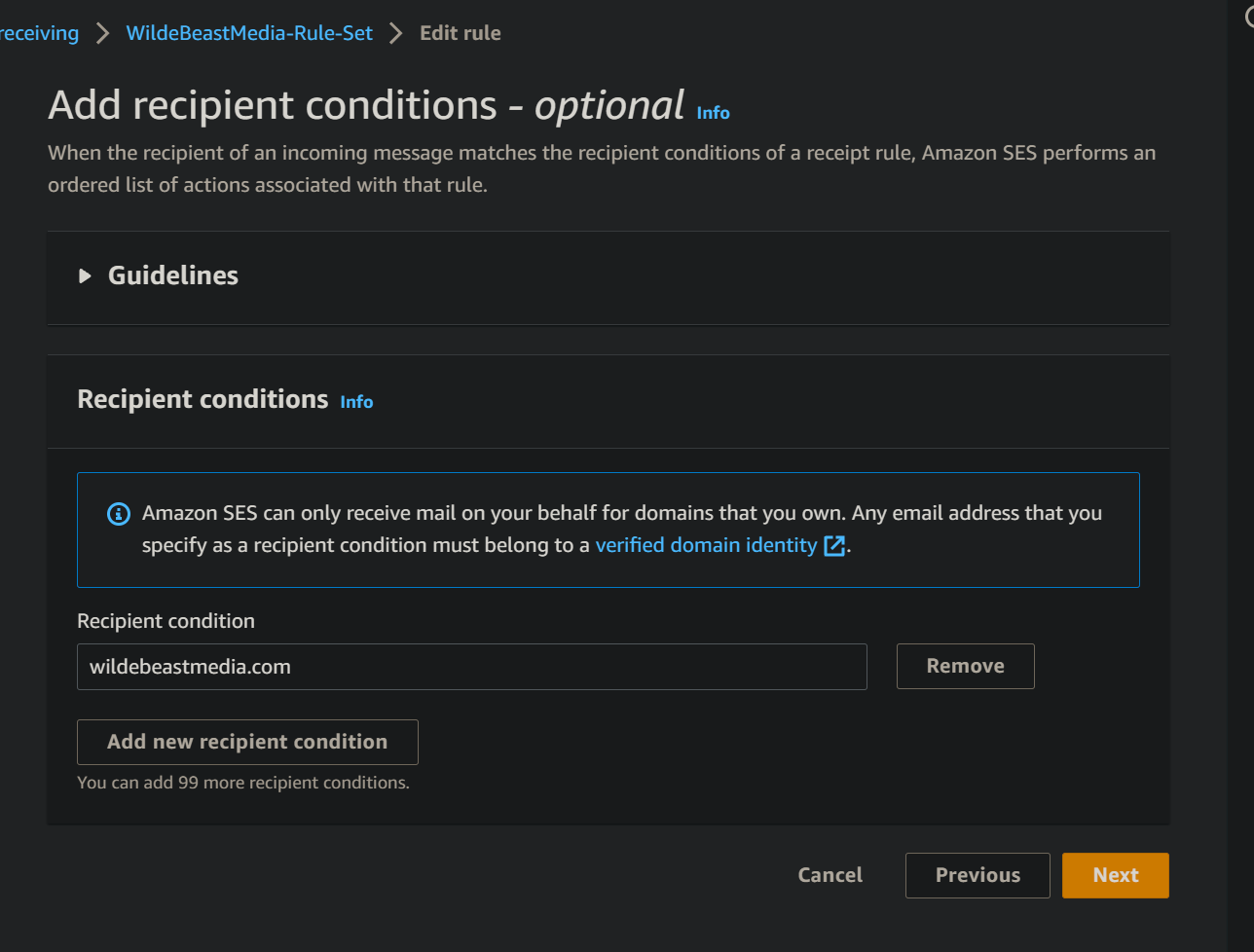
The recipient condition should be your domain name.
In the Receipt Rule, add an S3 Action. Set up the S3 Action to send your email to the S3 bucket that you created earlier. Then add a Lambda action to the Receipt Rule. Configure the Receipt Rule to invoke the Lambda function that you created earlier. Here is what those actions look like in the console:
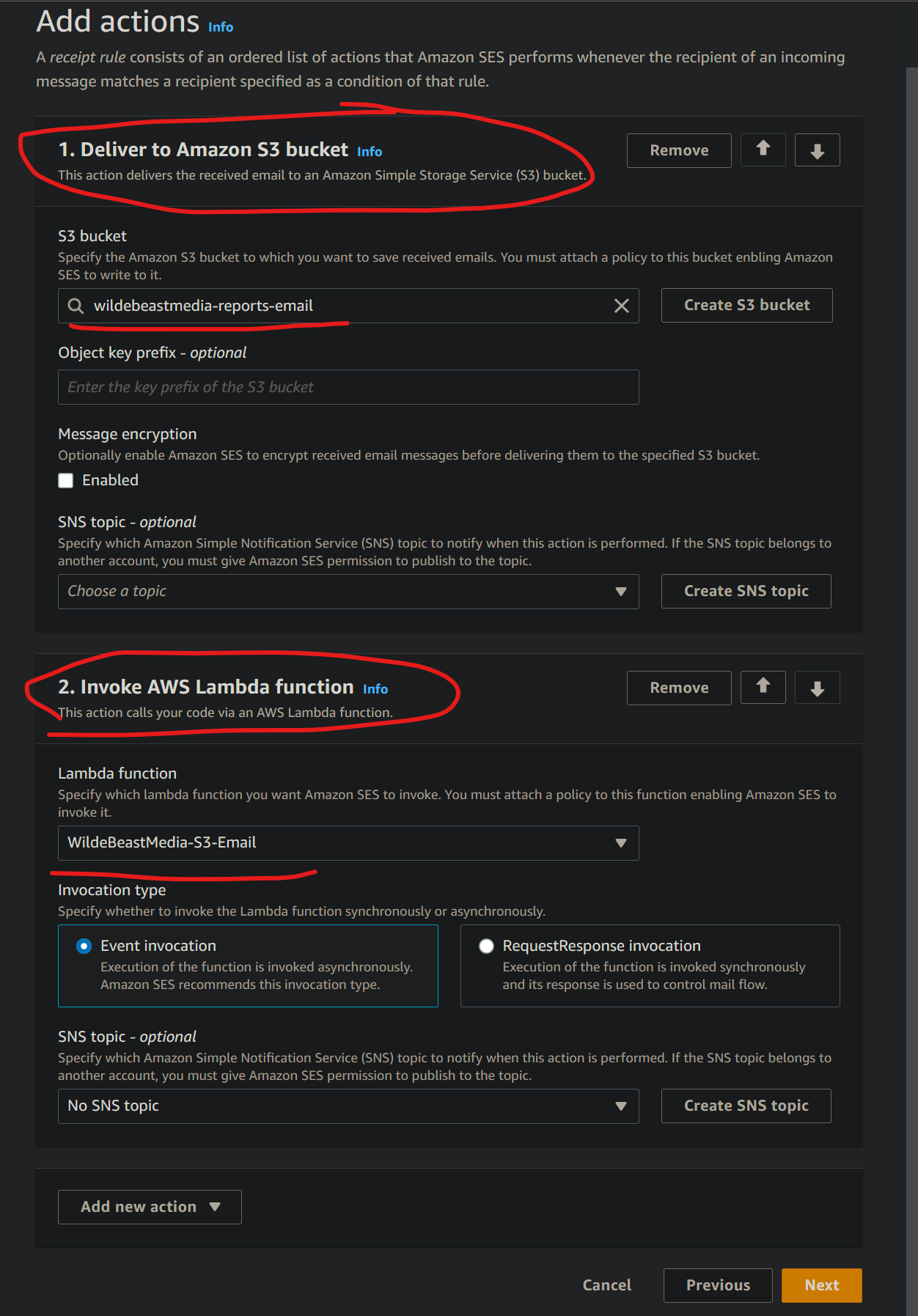
Final Working Result¶
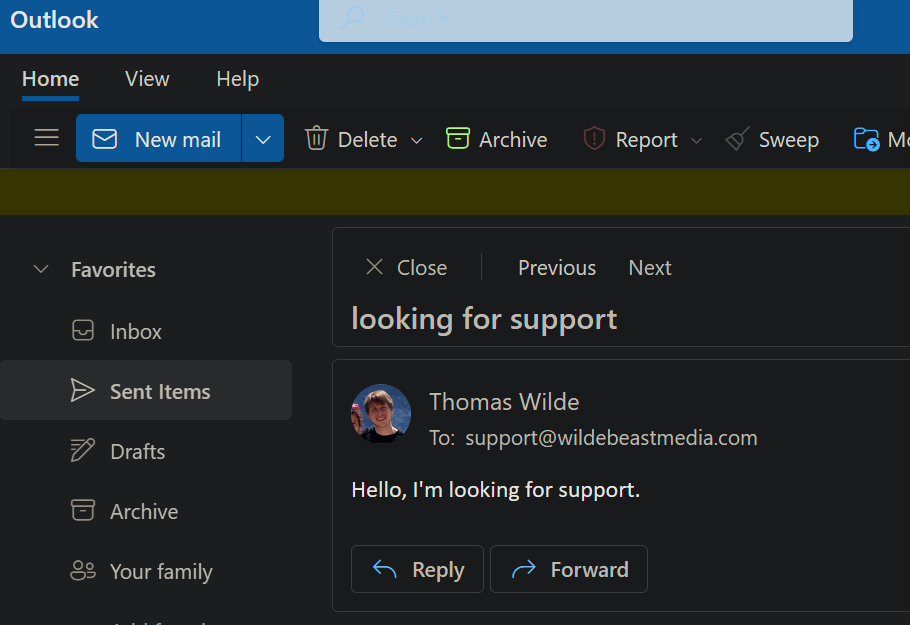
Let's send an email from a 'non-verified' email address (my hotmail), to the domain.
Here's what that email looks like
And here is the email that is sent from the Lambda function to our Gmail.
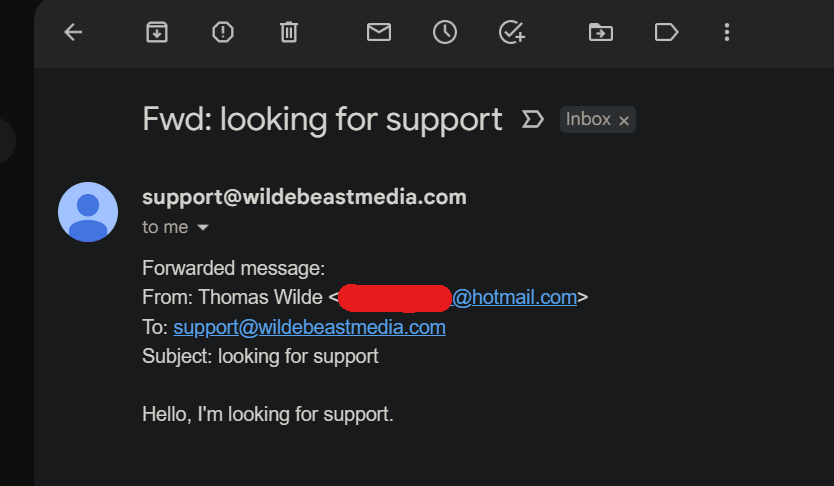
Now if I wanted to reply to the email as [email protected], I would just have to set up an alias and configure it in gmail.
While this method is not quite as desirable as a dedicated workplace client, such as Zoho, this is effectively a free way to receive emails to all of your domain names, which generally is not possible with dedicated workplace clients. However, I will also show you how to create a Zoho account to send and receive emails from your domain. Zoho is great because it lets you set up an account for free for one domain.